In this article, we will present you with a list of 6 specific tasks whose automation will give you the fastest return on investment when you're struggling with pressure to increase competitiveness, efficiency, and staffing shortages. Well-implemented production robotization can eliminate many bottlenecks in your company. Let's check which positions and processes in your facility could be improved today by well-implemented industrial robots.
Production process robotization - is it worth investing in it now?
Before we move on to the list of production processes, let's pause for a moment on the sense of investment and what measurable benefits it brings. Production process robotization doesn't mean employment reduction – it's primarily intelligent delegation of specific production tasks to machines in order to:
-
Increase efficiency – robots work faster and without breaks, so you gain additional production capacity.
-
Stable quality – elimination of human errors reduces the number of defects and complaints.
-
Safety and human relief – machines replace humans in repetitive tasks, and workers can focus on more responsible operations.
-
Resistance to staff shortages – robots don't get sick and don't leave for the competition.
Well-selected production process robotization in SMEs can pay for itself within several months, bringing not only financial return but also real process optimization.
Manual operations are slow and generate errors. Finding a good welder or CNC operator often borders on a miracle, and pressure on prices and deadlines grows every quarter. Competition doesn't sleep – those who are already investing in production robotization are pulling ahead of the rest of the field.
Production process robotization - which process to choose as the first?
Choosing the first workstation for automation cannot be left to chance, as it is a key element of the entire implementation strategy.
It's worth emphasizing right away: robotization doesn't mean replacing the entire production line. Most often it's a surgical intervention – automating one specific element of the process that is most repetitive, non-ergonomic, or constitutes a bottleneck. A robot can, for example, perform only the welding operation, while preparation and reception of parts is still handled by humans.
Instead of guessing, answer a few simple questions. The process that is the best candidate meets most of these criteria:
-
Repeatability: Do employees perform the same movement hundreds of times a day? Ideal work for a robot.
-
Bottleneck: Is this the stage that slows down the entire production and generates delays?
-
Health and safety and ergonomics: Is the task burdensome, dangerous, or performed in harmful conditions (dust, fumes, noise)?
-
Labor costs: Does this position consume a significant portion of the payroll budget?
-
Ready solutions: Are there proven, almost "box" robotic workstations available on the market for this task?
-
Fast return (ROI): Does a simple calculation show that the investment has a chance to pay for itself in several months?
If you answered "yes" to most questions, you've just found your candidate #1.
TOP 6 production processes to start production robotization with
Which processes are worth robotizing first? Let's focus on processes that have the greatest impact on business and increasing efficiency while the implementation risk is minimal.
1.Welding of a given part using TIG, MIG/MAG methods
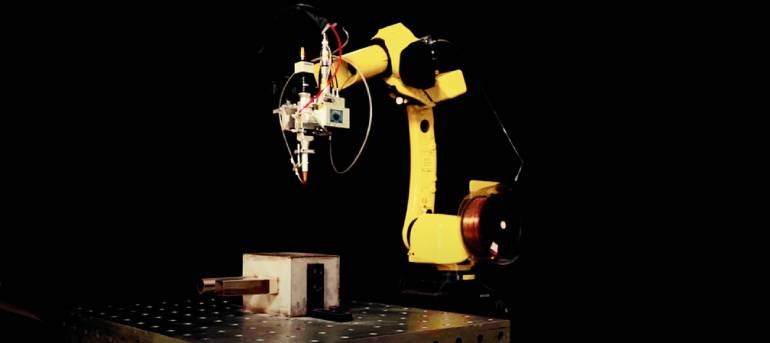
We're talking here not only about the welding process itself, but about automating the entire workstation – from picking up components to putting down the finished part. A welding robot lays a perfectly repeatable weld every time. By robotizing this process, you free up scarce welders from monotonous work, and they can take on more complex tasks.
Of course, the scope of automation can be flexibly adjusted. For many companies, the first, completely sufficient step is robotizing the actual weld laying process, while loading and unloading operations remain on the worker's side. This scalability is one of the greatest advantages of modern robotization.
We're talking about automating the entire workstation. The robot doesn't just lay perfectly repeatable welds. It can also pick up components itself, place them in a positioner, and put down the finished part. As a result, the scarce welder stops being a "torch operator" and becomes a supervisor of an efficient production cell, overseeing their proper operation and preparing subsequent orders.
-
Why as first? Because it's a classic bottleneck. The process is repetitive, labor-intensive, and burdened with health and safety risks. There are plenty of ready, refined welding cells on the market that can be implemented in a few weeks.
-
What do you gain (KPI/ROI)? Efficiency increase of even several dozen percent. Drastic reduction in defects. Stable, predictable quality.
One example of such a ready solution that allows for quick implementation and achieving immediate benefits is our robotic welding cell. Check: Fanuci 5.0 Turnkey welding robot.
In most facilities, welding is a critical point – it requires qualified people, generates the most errors, and slows down production.
Welding robotization (using laser technology) solves several problems simultaneously:
-
increases work speed up to 10 times compared to TIG or MIG/MAG methods,
-
ensures weld repeatability (fewer corrections, less waste),
-
reduces consumption of additional materials (savings on shielding gas up to 30–40%).
Thanks to this, robot welding becomes one of the fastest-paying implementations.
Such a large efficiency jump is possible thanks to modern technologies. To delve deeper into the fastest and most accurate methods, read our laser welding guide.
2.Grinding, polishing, deburring
After welding, elements need to be finished – ground, polished, spatter removed. This is burdensome work: dirt, dust, noise, and risk of errors. Manual grinding is slow, it's easy to damage the part, and often this is what slows down the entire production.
Grinding and polishing robots take over this work. Thanks to force sensors and vision systems, they can adjust pressure, find places requiring machining, and repeatably perform the same trajectory – regardless of whether it's a simple surface or complex curvature.
-
Every element is machined the same way – without risk of "over-grinding".
-
The entire production line works faster because the bottleneck disappears.
-
Workers don't have to inhale dust for hours or endure vibrations.
-
The company gains higher quality, fewer defects, and greater efficiency.
This is a natural step after welding automation – thanks to this, the key stage of metal machining becomes fully repeatable and automated. Robot costs are decreasing, and new solutions allow quick adaptation to different parts, so grinding robotization becomes available also for small and medium production facilities.
3.Bending and forming
Bending and forming of sheets and profiles is one of the key stages in metal production. This process requires not only physical strength but above all precision. The smallest error in sheet positioning can mean rejection of an entire batch. No wonder that robotization is increasingly used here.
Robotization eliminates the biggest pain points of traditional bending. Instead of two workers lifting heavy sheet metal, the robot lifts the sheet itself and precisely positions it under the press. Thanks to sensors and special grippers, it feeds parts always in the same way, reducing the risk of errors or accidents.
Where there was a shortage of operators, robots ensure production continuity – they can work without breaks, also on second and third shifts. Robotic workstations guarantee repeatability: each element has an identical bending angle and there's no material waste due to poor positioning.
Moreover, modern systems automatically correct parameters in real time (e.g., differences in material thickness), so product quality increases and waste decreases. As a result, bottlenecks disappear, efficiency increases, and people don't have to risk their health or tire physically – they can take on supervisory and organizational roles.
Bending robotization is an answer to the three biggest production problems: lack of people to operate machines, risk of errors and accidents, and limited efficiency. Thanks to it, heavy, dangerous, and precision-requiring work becomes fast, repeatable, and safe, taking place with minimal human involvement.
4.Cutting and sheet metal machining
Manual cutting or even semi-automatic machines are not enough today. Robotic laser cutting provides:
-
accuracy of 0.1 mm,
-
smooth edges without the need for additional machining,
-
minimal material losses.
Precision and minimal material losses are the domain of modern cutting machines. Want to understand how this technology translates into real savings and return on investment? Read: Why fiber laser is a good investment?
This is a process where every second and every millimeter matters – especially with large production volumes. A robot feeding and receiving parts from the machine is the simplest way to increase its utilization. It can work during second and third shifts, without supervision. One worker, instead of operating one machine, can supervise an entire production cell on the production floor.
-
Why as first? You eliminate micro-downtime between cycles and make production independent of people's availability. This is critical with current staff shortages.
-
What do you gain (KPI/ROI)? More pieces produced per day from the same expensive machine. Less dependence on shift schedules.
Production process robotization in CNC machine operation involves using a robot that will feed and receive parts. Thanks to this, the machine can work continuously, without breaks. Cobots are easy to program even for inexperienced personnel.
5.Palletizing and packaging
Arranging boxes, bags, or finished components on pallets is heavy, monotonous, and non-ergonomic work. A robot performs these repetitive activities faster, more precisely, and without risk of spine injuries, being irreplaceable in performing both simple and more complex movement sequences. All this makes palletizing and packaging one of the common production processes for which industrial robots are used. Why?
-
it's a repetitive activity with little added value (moving an object from A to B),
-
the burden on humans is high (e.g., tens of tons lifted during a shift) and leads to injuries,
-
ready, refined solutions are available – many companies offer standard palletizing robots along with tooling and software for quick implementation.
It's precisely in such applications, where the robot is supposed to be a flexible solution and often works in close proximity to humans, that collaborative robots work excellently. If you want to learn how they differ from traditional machines and what possibilities they offer, check our guide where we explain what cobots are.
Robotic palletizing frees workers from physical labor, giving the opportunity to move them to other activities like quality control. Palletizers are among the robots with the highest ROI. Palletizing and stacking work often engages several workers per shift. One robot can replace them all. Even if its work pace may be lower than a human's, thanks to the fact that it can work 3 shifts without breaks, it ultimately stacks more packages than a tired worker who needs breaks. It's estimated that return on investment in a palletizer can occur in just several months.
6.Automatic quality control
Why automate quality control? A human, even the greatest specialist, will never be able to check products with 100% attention. In this area, automation focuses on precision, and the robot minimizes the risk of complaints because it controls quality with equal attention regardless of work duration or product nature.
Benefits for workers: searching for scratches, damage, or precise measurements can be monotonous. A robot automating quality control will allow workers to focus on solving problems, improving processes, rather than performing tiring, repetitive activities with high risk of error.
Quality control automation in production companies from various industries is rarely the first robotization process in production because it only detects errors and doesn't speed up production.
Production process robotization - where to start the adventure with robots in a metal machining company?

Our experience and that of many production facilities show certain patterns worth considering. Most often, the first robot that appears in a company is a welding robot. The choice is often clear because it provides quick and multidimensional effects:
-
efficiency increase,
-
improvement of weld quality and repeatability,
-
work safety,
-
independence from the lack of qualified welders.
If welding constitutes a large part of your production, then investing in a welding robot may be the best investment direction.
The second very popular choice for robotization process is palletizing or machine loading. A palletizing robot will be an excellent choice when manual packaging and stacking goods on pallets engages many workers for many hours on each shift. Such a robot brings immediate benefits: from ergonomics and efficiency increase to real reduction of operational costs, because it relieves workers from the need to move hundreds of kilograms daily.
Summary: production robotization, what to robotize first
Production process robotization is a complex process that, however, when adapted to individual company needs, provides enormous benefits both in short and long term. At the beginning, find the most labor-intensive for people, repetitive, and burdensome tasks. This will help you find processes worth "delegating" to a robot. First successes and quick return on investment will certainly encourage you to expand the robotization scope to additional production processes.
At the start of this journey, it's crucial to use expert knowledge (e.g., experienced integrators who offer comprehensive services, complete support, and individual approach, helping choose appropriate equipment and plan implementation) and engage the team in learning new technologies. Thanks to this, even a small company from the metal industry can successfully enter the world of robotization, ensuring integration with existing systems and quick team adaptation to new technologies. So choose the process that most needs improvement and best fits your business goals, then give robots a chance – in a short time you'll be convinced it was the right decision.
In the article, we mentioned laser cutting and welding as processes ideal for robotization. If you want to learn how laser technology can revolutionize your production process, schedule a free, non-binding consultation with our expert. We'll help you assess the potential and select the best solution.