Contemporary market challenges – from personnel shortages, through growing demands for production flexibility, to the necessity of implementing sustainable practices – make the search for new, efficient solutions in metal processing a priority for every enterprise. It is precisely in this context that Industry 5.0 emerges – a concept that redefines the way of thinking about production and offers concrete solutions for your facility.
Evolution of Industry 4.0
The concept of Industry 4.0 first appeared in Germany in 2011, focusing on digitization and automation of production processes. It encompassed widespread application of technologies such as cloud computing, big data analysis, machine learning, robots, and the Internet of Things (IoT). The fourth industrial revolution aimed to achieve higher efficiency and productivity by connecting the physical world of machines with the virtual world of the Internet and information technologies.
However, as in every revolution, shortcomings also appeared. Industry 4.0 largely downplayed the human factor and the environmental and social consequences of mass automation. It is precisely these aspects that form the foundation for a new paradigm – Industry 5.0.
Industry 5.0 is not an entirely new revolution, but rather an evolution and continuation of digital transformation. It focuses on integrating humans and machines to increase efficiency and innovation, while simultaneously emphasizing the strengthening of social and ecological values. This means that modern technologies should not only increase productivity, but also improve the quality of life of workers and care for sustainable development.
Industry 5.0 vs. Industry 4.0: Key differences
Understanding these differences is crucial for companies in the metal processing industry that are planning further investments. Industry 5.0 offers a significantly broader perspective and concrete solutions for your current challenges in technological innovation.
Human at the center: Synergy with technology and the role of cobots

In Industry 4.0, there was a drive to minimize the human role in the production process, replacing physical work with machines and computers. The result was neglecting the impact of automation on human capital, threatening employment levels and overlooking the unique human contribution to high-quality production.
Industry 5.0 radically changes this approach, placing humans back at the center and emphasizing the human aspect in modern production. It is recognized that human experience, knowledge, and skills are fundamental resources ensuring long-term competitive advantage. The goal is to achieve synergy between humans and machines, where technology supports and enhances human work rather than replacing it.
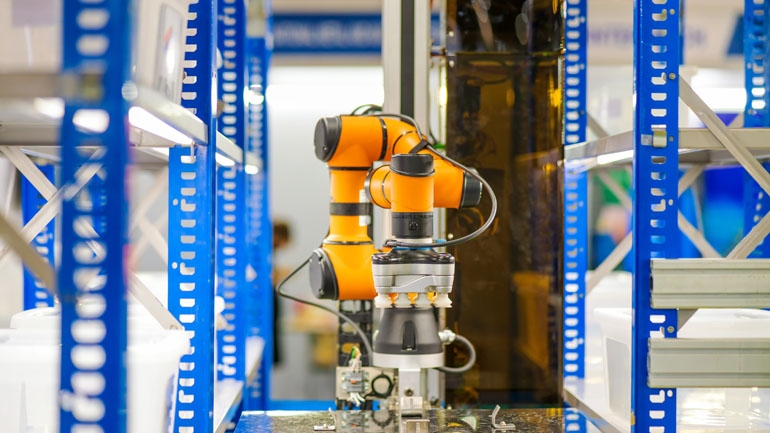
Cobots (collaborative robots) play a key role here, which are designed for direct, physical interaction with humans in the same work environment. Unlike traditional industrial robots, cobots automate repetitive, burdensome, and dangerous activities, such as long, simple welding seams, with precision that cannot be achieved manually. This allows workers to focus on more complex tasks, such as designing processes and products, problem-solving, organization, planning, or customer service. This leads to increased efficiency and quality, as the machine eliminates errors and fatigue in routine activities, while humans correct nuances and care for specific customer requirements. You don't have to worry that a new machine will take jobs away from your specialists – instead, it will enable them to focus on what's most important and make them even more efficient.
Sustainable development: Carbon footprint reduction and resource efficiency
In the era of Industry 4.0, environmental and social issues were often overlooked. However, in recent years, in the face of growing ecological problems, sustainable development has become a priority.
Industry 5.0 integrates social and environmental issues with business processes, based on three main pillars: sustainable development, resilience, and human orientation. It aims to ensure that industry will have a much smaller impact on the environment by reducing waste, supporting a circular economy, reusing materials, and consuming less energy in a more ecological way.
For your facility in the metal processing industry, this means concrete benefits in terms of optimizing production processes and environmental protection. Sustainable Industry 5.0 technologies promote optimization of energy and material consumption, which translates into real financial savings and compliance with growing ecological requirements. Intelligent control systems can significantly reduce energy and raw material costs, which constitute a significant part of expenses in the Polish metal industry thanks to savings resulting from better resource management. An example could be a fiber laser with automatic standby mode between cuts, which reduces power consumption by several dozen percent and supports renewable energy sources in the facility. Less material waste – through optimization of nestings or reduction of defects – means better profitability and fits into the idea of a circular economy and limiting negative environmental impact.
Modern laser technologies are an excellent example of energy-efficient solutions in the spirit of Industry 5.0. laser processing of metal sheets using the latest fiber systems allows for significant reduction in energy consumption while simultaneously increasing precision and cutting efficiency.
Resilience to challenges: Supply chain flexibility and cybersecurity
Current geopolitical and economic realities have shown how crucial enterprise resilience to sudden challenges is. Industry 5.0 directly addresses this need, striving to increase supply chain flexibility and strengthen cybersecurity in the production process.
In Industry 4.0, widespread connection of production machines to the Internet (IoT) as part of process digitization made them potential targets of cyber attacks, exposing companies to loss of strategic data and destabilization of processes. Industry 5.0 emphasizes that security and data protection are key challenges. This includes not only protection against hackers, but also care for privacy and self-determination of workers in the face of digital surveillance in the context of social priorities. For your facility, this means the necessity of choosing equipment and systems that offer advanced data protection strategies.
Implementing Industry 5.0 technologies equips an enterprise with the ability to quickly respond to market changes and adapt to individual customer needs. Companies with flexible production lines and advanced data analytics can more easily switch production to new products, personalize offers for customers, or deal with sudden supply chain disruptions. If demand for a specific metal component increases or an opportunity for prototyping for a new client appears, a factory operating in the spirit of Industry 5.0 is able to retool and adapt plans within hours, while competitors remain behind. This business agility is invaluable today.
Cobots – human-machine collaboration
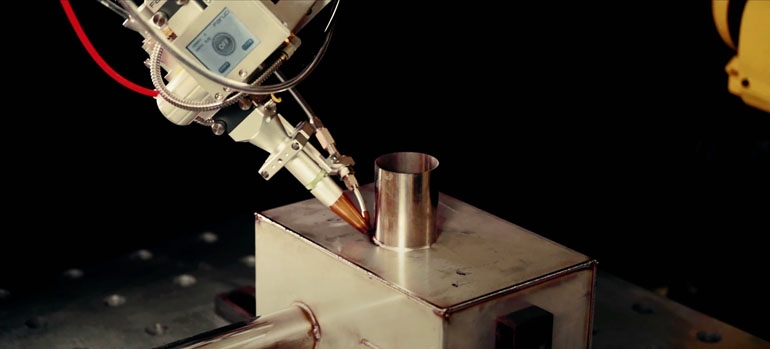
Cobots, or collaborative robots, are one of the most tangible examples of how Industry 5.0 changes everyday life in production facilities. These are robots designed for direct collaboration with humans in the same workspace, without the need for separate safety barriers, thanks to advanced sensor systems.
Their role in metal processing is invaluable:
-
Worker relief: Cobots perform burdensome, repetitive, and dangerous activities, such as long welding seams or machine operation, relieving human personnel from physical work.
-
Increased precision and efficiency: While a cobot performs tasks requiring repetitive precision, like welding, a human welder can focus on preparing the next element, quality control, or weld cosmetics, which significantly affects production efficiency. This division of roles improves both efficiency and quality, minimizing errors and fatigue resulting from routine activities.
-
Changing nature of work: Cobots don't replace workers, but change the nature of their duties, enabling effective training in new areas. Instead of physically demanding operations, personnel can concentrate on programming cobots, process supervision, technology improvement, or more creative tasks.
-
Increased safety: Thanks to built-in sensors, cobots can detect movement and human presence in their surroundings, which allows for safe coexistence at a shared workstation.
Such integrated systems represent the quintessence of Industry 5.0 philosophy, combining automation precision with flexibility of adaptation to various tasks. Check: Fanuc 5.0 Turnkey welding robot and see how modern solutions can revolutionize welding processes in your facility.
As a result, cobots provide an answer to the problem of shortage of qualified physical workers, and also help retain the expertise of older staff, filling gaps and changing the work profile to a more valuable one.
Industry 5.0 technologies changing metal processing
Industry 5.0 is based on advanced technologies that combine advanced technologies known from Industry 4.0 with a new concept oriented toward humans and sustainable goals. Here's how specific solutions can revolutionize metal processing in your company:
Automation and robotization: A new era of precision and efficiency
In the era of Industry 5.0, automation goes beyond simple replacement of human work, becoming a tool to achieve unprecedented precision and efficiency while simultaneously supporting humans within innovative solutions.
-
Cobots: As already mentioned, they are the quintessence of this new era, enabling direct, safe human-machine collaboration and relieving workers from monotonous or dangerous tasks in metal processing, such as loading/unloading, welding, or polishing.
-
Digital twins: These are virtual models of your machines, production lines, or entire halls that reflect their operation in a computer and are crucial for optimization. In the metal industry, a digital twin can simulate the work of your CNC machining center, welding robot, or laser cell.
Practical application: Thanks to this, engineers can test and optimize processes on a computer screen within virtual workshops – check collisions, select cutting/welding parameters, schedule operations – without the risk of stopping real production. Such simulation allows detecting errors and bottlenecks before they occur physically, which shortens the time for launching new processes and reduces material losses. This is precisely that "Ooooh great!" that accelerates innovation and reduces experiment costs. -
Artificial intelligence (AI) in process analysis: AI plays a dual role: first, it analyzes huge sets of production data (temperatures, vibrations, machine performance, cycle times, quality inspection results, etc.) within advanced data analysis and draws conclusions from them that are invisible to the naked eye; second, it supports automatic decision-making at the operational level.
Specific examples in metal processing: AI can optimize the production plan for a given shift, taking into account changes in order priorities and raw material availability – something that a planner used to do in a few hours, an algorithm can now do in a few minutes thanks to integration with IT systems. Another application is AI-based vision systems for quality control of welds or edges after laser cutting: a camera scans details in real-time, and a neural network detects defective welds or deformations much faster than an inspector, rejecting defective pieces or signaling the need to correct process parameters and solving technical problems.
Practical path: Many of these AI solutions are already available as modules for existing MES/ERP systems or as cloud service solutions, which facilitates their implementation even in traditional factories through a new approach to technology.
Diagnostics and monitoring: Failure prediction and resource optimization
The key to increasing production efficiency is minimizing unplanned downtime. Here, diagnostics and monitoring in the spirit of Industry 5.0 come to help.
-
Predictive maintenance: Data analysis, sensors, and predictive algorithms are used to predict moments when equipment may require maintenance or repair using energy-efficient solutions. This contributes to minimizing downtime during production and optimizing efficiency. Digital twins, connecting with IoT data from machines, can continuously analyze their condition and forecast failures, e.g., detecting increasing spindle vibrations signaling bearing wear and planning replacement at a convenient time within a sustainable approach to maintenance. Thanks to this, you can plan service when it is least invasive to your schedule, instead of reacting to sudden failures.
-
AI in resource consumption optimization: Artificial intelligence not only analyzes quality data but also supports demand prediction and optimal resource utilization in the context of increasing competitiveness. By analyzing order trends, inventory levels, and machine efficiency, AI can recommend, for example, changing the sheet production schedule to avoid overproduction of waste or downtime, thereby supporting energy storage and resource optimization. This allows for better cost management and more sustainable production.
Intelligent intralogistics: Flow optimization and resource management
Efficient intralogistics is the bloodstream of every production facility. Industry 5.0 provides tools that make the flow of materials and information faster and more efficient through the use of intelligent networks.
-
Internet of Things (IoT): These are devices equipped with a range of sensors that can acquire and exchange data between themselves without human participation within machine integration. Implementing IoT in your facility will allow for more efficient execution of production processes and more effective equipment utilization. Think of intelligent warehouses that monitor inventory levels themselves, or machines that communicate with each other to optimize processing sequence within sustainable solutions.
-
Big Data analysis: Large data volumes are valuable sources of information, and technology enables the introduction of advanced analytical systems. Their analysis allows for more efficient process management, creating systematic databases that give a complete picture of performance and work rhythm. You can identify bottlenecks, optimize transport paths within the facility, and plan more precisely.
-
Internal transport automation: Although sources don't focus on intralogistics in metal processing, they mention autonomous delivery robots and the possibility of using AI for efficient inventory and delivery management in the context of cooperation with business partners. In practice, this means that autonomous vehicles (AGV) can move in your facility, independently transporting details between workstations without engaging workers, supporting augmented reality in logistics management. This relieves people and minimizes the risk of transport errors.
Industry 5.0 in practice: examples from Polish facilities
The Polish metal processing industry faces a unique opportunity to utilize the potential of Industry 5.0.
-
Growing robotization: Poland is gaining importance in robotics, with an increasing number of robots used in industry, including automotive and manufacturing. This trend naturally transfers to metal processing, where precision and repeatability of robots are extremely valuable.
-
Digitization and automation in numbers: Studies of Polish enterprises already in 2019 showed that a large part of companies use ERP software (65.7%) and use cloud computing (31.9%) within process digitization. Moreover, 12.6% acquired Big Data, and 5.2% used their analyses. Among enterprises producing machines and equipment, 9% manufactured machines capable of working in direct contact with humans, and 7.1% equipped them with additional sensor systems. This shows that the foundations for Industry 5.0 in Poland already exist.
-
Production personalization: Already 17.5% of surveyed Polish enterprises enabled customers to individually compose orders through a website or application. Importantly, 2% had production lines that automatically processed and commissioned such personalized orders without human participation. In the metal processing industry, this means the possibility of quick and efficient adaptation of production to very specific customer requirements, which is crucial in today's market.
-
Benefits from implementations: Polish companies that have already invested in Industry 4.0 technologies (which are the foundation of 5.0) record significant benefits thanks to savings resulting from process optimization. Big Data analysis and artificial intelligence translate into productivity growth, cost reduction, improvement of quality and data security. Enterprises that recorded increased spending on these technologies showed higher competitiveness ratings both nationally and globally. This is a clear signal that investments in intelligent technologies bring real, measurable results.
These examples show that Industry 5.0 is not a distant vision, but a real development path for Polish companies in the metal processing industry, which brings concrete improvements and increases efficiency.
Challenges and perspectives for Polish industry in the context of Industry 5.0
Implementing Industry 5.0 is a complex process, involving both significant challenges and promising perspectives for Polish industry. A conscious approach to both these aspects is crucial.
Challenges:
-
Lack of qualified human capital and the need for retraining: This is paradoxically the biggest challenge and simultaneously an impulse for change. Poland, struggling with population aging, faces a projected decline in labor supply by more than 1/3 by 2070. Already today there is a shortage of qualified physical workers and engineers. Implementing new technologies requires new skills – digital, technical, and soft, and massive upskilling and reskilling are necessary. Many managers still don't understand AI concepts, which holds back implementations.
-
Implementation and maintenance costs: Introducing advanced AI systems, robotics, and digital twins requires significant investments. Many companies cite high costs as the reason for not using AI or IoT.
-
Data security and cyber threats: Increasing system integration and connecting machines to the Internet (IoT) makes strategic production data vulnerable to cyber attacks. Data security concerns are often cited as reasons for not using cloud computing or the Internet of Things. New occupational risks also concern safety and ergonomics in human-robot interaction and issues of privacy and self-determination in the face of digital surveillance.
-
Employee acceptance and concerns: People often experience fear of new technologies due to unfamiliarity with their capabilities. Lack of enterprise efforts to familiarize people with new technologies and encourage integrated work may cause resistance in the future. In Industry 5.0, social dialogue and employee engagement are crucial so that digital solutions support rather than replace human work.
-
Ensuring AI ethics and avoiding bias: AI development requires principles such as transparency, fairness, and harm avoidance. Care must be taken for equal treatment and elimination of bias in training data so that technologies don't reinforce stereotypes or inequalities.
Perspectives and opportunities:
-
Dramatic improvement in efficiency and quality: Combining automation with intelligence (AI) and human creativity leads to significant productivity growth, better product quality, and reduced risk of errors and downtime. For metal processing, this means more cut or welded components per shift, virtually zero dimensional deviations, and improved product durability thanks to process repeatability.
-
Greater flexibility and innovation capacity: Early implementation of Industry 5.0 technologies equips enterprises with the ability to quickly respond to market changes, personalize offers, and deal with supply chain disruptions. Digital tools allow testing new ideas (e.g., new constructions or material joining techniques) without disrupting current production.
-
Better resource utilization and sustainable development: Intelligent systems optimize energy and material consumption, leading to real savings and compliance with growing environmental requirements. Companies adapting to environmental standards will avoid penalties, gain business partner favor, and become more attractive to investors and young talent.
-
Increasing industry attractiveness for young generations: Industry 5.0 can make production more attractive to young and older people, which will help solve the problem of lack of qualified human capital and retain specialist knowledge.
-
Government and EU support: The European Commission formally presented Industry 5.0 as a key step toward sustainable and inclusive industrial development. There are and are developing programs supporting innovation and development. European policies such as the Green Deal or EU industrial strategy provide frameworks for the Industry 5.0 vision.
-
Cooperation and social dialogue: Employee participation and social dialogue are crucial for utilizing Industry 5.0 opportunities, requiring engagement at all levels. Public-private partnerships and cooperation between universities and enterprises are necessary for developing educational tools, programs, and exchanging good practices.
In summary, although the path to full Industry 5.0 implementation in Poland will require significant efforts and investments, especially in human capital development and infrastructure, the offered benefits in terms of efficiency, resilience, and sustainable development are invaluable.
Industry 5.0 – the future of efficiency and sustainability in metal processing
For anyone looking for new metal processing equipment that will streamline processes and increase production efficiency, Industry 5.0 is more than just a trendy slogan – it's a real answer to contemporary market challenges. It is a qualitative breakthrough in the Polish metal processing industry that enables combining the power of technology with the irreplaceable value of human experience and creativity.
This is not a revolution that aims solely to replace humans with machines. On the contrary, Industry 5.0 puts humans at the center, recognizing their role in innovation and problem-solving, and treats technology – from cobots, through digital twins, to artificial intelligence – as a tool supporting and enhancing their capabilities.
The path to full Industry 5.0 implementation is demanding – both technically and organizationally – however, the benefits in terms of higher productivity, better adaptability, and lasting competitiveness are invaluable. Companies that start combining human potential with the latest technologies now will gain the status of leaders, creating factories of the future today.
Want to check how Industry 5.0 technologies can revolutionize your production? Schedule a free consultation and discover which solutions – from cobots to AI – will be best for your facility. Our experts will analyze your processes and show concrete benefits you can achieve.
Bibliography
-
EUR-Lex. (2025). Information and notices (C/2025/108). Official Journal of the European Union. https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/PL/TXT/PDF/?uri=OJ%3AC_202500108
-
Statistics Poland. (2023). Industry 4.0 in Poland. Final report. https://stat.gov.pl/files/gfx/portalinformacyjny/pl/defaultaktualnosci/6337/13/1/1/raport_koncowy_przemysl_4.0.pdf
-
Ślusarczyk, B. (Ed.). (2023). Horizons of artificial intelligence and industry 5.0. WSB Academy. https://wsb.edu.pl/files/news/13476/sk_horyzonty_sztucznej_inteligencji_a_przemysl_50_ebook_1403.pdf
-
Kaczmar-Kolny, E., & Pośpiech, W. (2022). Analysis of the impact of digitization on organization management. Scientific Papers of the Department of Computer Science in Industry. https://kip.ubb.edu.pl/download/.../04_kaczmar_kolny_ewa_pospiech_wojciech_analiza.pdf
-
Hamera, A. (2024). The role of user experience in the era of industry 5.0. Enterprise Management, 27(2), 7–15.